| |
Introduction
There are 30 different types of lymphocytes (CD designations)
that make up the immune system. A balanced functioning of these
white blood cells keeps a person healthy. Two of these cell types
can cause infertility, implantation failures and miscarriages (see
diagram below). Women are born with these cell types. In some women,
they increase in numbers and activity and result in reproductive
failures.
| |
The Immune System
has 30
Different Kinds
of Lymphocytes |
| |
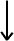 |
| |
Two Types Can
Damage
Pregnancies |
| |
 |
 |
Antibodies to Hormones
(Chapter 2) |
Tumor Necrosis
Factor Alpha
(Chapter 1) |
Antibodies to
Neurotransmitters
(Chapter 2) | |
Types of white blood cells include the following:
- TH-2 ("T Helper 2")
The response is a balanced
correct response during pregnancy (Category 1).
- TH-1 ("T Helper 1")
The response is a cyto-toxic
autoimmune response that can lead to infertility, implantation
failure and miscarriage (categories 2, 3, 4 and 5).
- CD3, CD4, CD8
Control production of blocking
antibody response; a correct response.
- CD19+ 5+
Produce
antiphospholipid antibodies (Category 2) and anti-DNA and
histone antibodies (Category 3). It also produces antisperm
antibodies.
- CD56+, CD57+
Are natural
killer cells.
Please see A Guide to Interpreting the Results of the
Reproductive Immunophenotype for more information on lymphocytes.
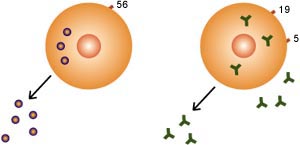
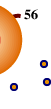
Chapter 1: CD 56+ Natural Killer CellsProblem
- Increase in number 2-12% normal. Above 12% see infertility and
pregnancy losses.
- Increase in cytotoxicity in NK assay. Cytotoxicity above 15%
at 50:1 can damage the embryo.
- These cells usually reside in the blood; however, in 2% of
women they are so activated they live in the uterus. This is
determined by an endometrial
biopsy on day 26 of a normal cycle and by the TJ-6 test which
finds women whose Natural Killer Cells have become the most
activated.
- They produce toxic Cytokines (TH-1 cytokines) including Tumor
Necrosis Factor (TNF) Alpha.
Consequences
- Prevent implantation.
- Cause miscarriages by damaging the placental cells, causing
decidual necrosis, damage the yolk sac.
- Later in pregnancy they cause slowness of the heart rate of
the baby, cause an irregular shaped gestational sac that is
smaller than normal and amniotic fluid volume that is too small.
- They induce subchorionic hemorrhages which can cause spotting,
bleeding and can be seen easily on ultrasound.
- In some women they can affect the DNA in the eggs so that
fragmentation, slow cell division, arrested cell division and poor
quality embryos are seen.
Chapter 2: CD 19+5+ B Cells
(1)Problem
- Normal numbers are 2% - 10%. Women with problems have
increases in cell numbers above 10%.
- These cells produce antibodies to hormones necessary for
pregnancies to develop safely. These antihormone antibodies are
against estradiol, progesterone, and Human Chorionic Gonadotropin
(HCG).
- These antibodies lower hormone levels and lead to luteal phase
deficiencies, slow rising HCG levels when pregnant, poor
stimulation during ovulation induction cycles and poor lining
development by ultrasound evaluation.
At
Ovulation or Recovery of Eggs |
| |
|
|
TNF |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| DNA in Eggs |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
Damages DNA in Eggs by
Apoptosis - Spot Welds the DNA so that it Divides
Poorly |
|
|
 |
 |
|
|
Egg |
Embryos Show Slow Cellular
Division, Fragmentation of Cells, Inclusions in Cells. This
Causes Failed IVF, Implantation Failure & Ovarian
Failure |
Before
Implantation |
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
NK Cells Resident in
Uterus |
| |
 |
 |
|
| TNF Alpha |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
| |
 |
 |
Causes Apoptosis of the DNA in
the Embryo
Leading to
Spot Welding of the DNA
Embryo Grows Slowly and
Dies.
Embryo Never Attaches.
Placental Tissue Grows
With
No Embryo Seen. |
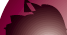
After
Implantation TNF Alpha Damage |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
| TNF |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
| Decidual
Necrosis |
 |
 |
 |
Yolk Sac Damage |
| Subchorianic
Hemorrhage |
 |
 |
Slow Heart
Beat |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
Irregular
Shape Gestational Sac |
| Placental
Cell Death |
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
Too Little Amniotic
Fluid |
Consequences
- Resistant ovary syndrome or premature ovarian failure. Day 3
FSH and Estradiol levels are too high.
- Poor egg quality in IVF. Fewer eggs recovered, slow division
following IVG, fragmentation of embryos, poor quality embryos,
fragile when frozen and thawed, multiple failed transfer cycles
with no positive BHCG or slow rising BHCG.
- Lining fails to develop adequate thickness, adequate layers or
adequate blood flow to zone three.
Chapter 3: CD 19+5+ B Cells
(2)Problem
- Normal numbers are 2 - 10%.. Women with problems have
increases in cell numbers above 10%.
- Produce antibodies to neurotransmitters, including serotonin,
endorphins and enkaphlans.
- These antibodies cause the ovaries to be resistant to
stimulation, cause a poor lining to develop, interfere with the
muscle development of the uterus, and prevent blood flow to the
lining of the uterus and muscle at the time of implantation.
- These antibodies can cause depression, fibromyalgia, sleep
disorders, increasing PMS symptoms and night sweats.
Antibodies to
Neurotransmitters |
|
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
 |
 |
Zones 1, 2
& 3 of endometrium on day of ovulation |
| Muscle cells |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Serotonin |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Blood flow
to Zone 3 |
 |
Endorphins
& enkaphlins are involved in the modeling of the 3 layers
of endometrium
Antibodies to these lead to a thin
"teflon" endometrium without a blood supply |
Serotonin needed to change muscle cells of
uterus to accommodate a pregnancy
Antibodies to serotonin
leads to a uterus that does not accommodate a
pregnancy |
 |
|
Consequences
- Follicles stimulate poorly and require heavy doses of
fertility drugs to awaken.
- Endometrial lining is thin; it rarely gets above 7 mm.
- Three zones of the endometrial lining do not develop.
- Blood vessels do not enter zone three.
- Uterine smooth muscle remains quiet and does not contract
three times in two minutes.
- Eggs are of poor quality, fertilize in vitro with difficulty,
divide slowly or incompletely, are low grade embryos and embryos
fragment.
- Women are depressed, sleep poorly, panic easily and experience
symptoms of achiness and fibromyalgia.
|