Antiphospholipid Antibodies
Repeated miscarriages, IVF failures, endometriosis and anything
that causes tissue injury can lead to the formation of antibodies to
phospholipids. These are called antiphospholipid antibodies.
Phospholipids are important molecules in the membranes of all cells,
and antibodies to these important molecules can derange cell
function, cause inflammation and can even cause blood to clot too
quickly.
Many patients with autoimmune diseases also have tissue injury
and make antiphospholipid antibodies. This is how antiphospholipid
antibodies were discovered. Certain patients with lupus made
antibodies that caused their blood to clot too quickly. This
antibody is now called the "lupus anticoagulant antibody." When the
test for this antibody is positive, most people think they have
lupus. However, in our experience, the majority of patients with
this antibody have produced it because of infertility, IVF failures
or recurrent pregnancy losses, not because they have lupus or other
autoimmune diseases.
In our experience 22% of women with recurrent pregnancy losses
have antiphospholipid antibodies. The incidence of this problem
increases in women by 15% with each pregnancy that is lost. It is a
significant consequence of infertility, implantation failures and
recurrent pregnancy losses.
There are six different phospholipid molecules that have very
important functions in cell membranes and intracellular organelles.
The phospholipid molecules are
- Cardiolipin
- Ethanolamine
- Glycerol
- Inositol
- Phosphatidic Acid
- Serine
Cell death or cell injury can lead to the production of
antibodies to all or any one of these molecules. These antibodies
disrupt cell functions and increase the clotting speed of blood.
This can cause chaos early in pregnancy.
The antibodies first produced are called gamma globulin M (IgM).
These antibodies circulate in the blood and protect the blood
environment. As the problem get worse, the IgM antibodies mature and
produce gamma globulin G (IgG). These primarily in the lymphatic
system and the lymph nodes. IgG antibodies go on to produce gamma
globulin A (IgA), as the immunity completes its development. The IgG
antibodies live in and protect the organs, including the
reproductive tract.
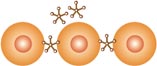
As shown in the diagram, Serine and Ethanolamine are
phospholipids that serve as glue molecules in allowing the placenta
to be securely attached to the uterus during implantation. They also
allow the cytotrophoblast to change into a new cell, the
syncytiotrophoblast, which begins to feed the baby by transporting
nutrition from the mother's blood into the baby.
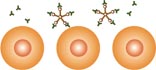
Antibodies to these phospholipids prevent secure attachment or
often totally prevent attachment. In addition, antibodies to these
phospholipids prevent the cytophoblast from forming into the
syncytiotrophoblast, which is needed to feed the baby. We have found
that when this problem is diagnosed there is now a reason that is
97% effective in causing pregnancies to fail early.
Cytotrophoblast Placental
Cell
Function: Attaches placenta to
uterus. |
 |
 |
| Phospholipid |
Antiphospholipid Antibody |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Syncytiotrophoblast |
Delayed Formation of Syncytiotrophoblast |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Function:
- Feeds the baby.
- Produces ß-hCG and progesterone.
- Grows throughout pregnancy.
|
Pregnancy loss or implantation
failure. |
|