| |
|
|
 |
Category 1 : Immunological Problems |
 |
| |
HLA Compatibility as a Cause for Recurrent Spontaneous Pregnancy
Loss
The HLA antigens on the placenta cells made by the father are
called HLA-G. When the couple shares DQ alpha antigens in common,
the G molecule put on the placental cells by the father is too
similar to the G molecule that the woman's father put on her
placenta to sustain her in her mother's uterus.
As a result, she does not make the blocking antibody, the baby
dies, and her immune system recognizes the placenta as "altered
self" (i.e., a cancer cell) and category 1 problems move on to
worsen to categories 2, 3, 4 and 5 (see diagram
below).
Consequences
- Inadequate blocking antibody formation.
- Ineffective camouflage of placenta.
- Placental cells fail to grow and divide.
- Death of placental cells.
- Activation of category 2, 3, 4 and 5 immune problems.
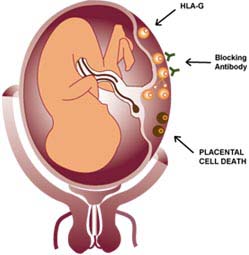
HLA-G: Message sent
from father to stimulate blocking antibody.
Blocking Antibody:
Protects and stimulates the growth of placental cells.
Placental Cell
Death: Consequences of low blocking antibody.
|
|
 Consequences
of Recurrent Pregnancy Loss
: An Introduction to
Categories 1 - 5 Immune Problems Consequences
of Recurrent Pregnancy Loss
: An Introduction to
Categories 1 - 5 Immune Problems |
|