Positive Antinuclear Antibody (ANA)
Category 3 immune problems occur in 22% of women with recurrent
pregnancy losses and nearly 50% of women with infertility and IVF
failures. Women with this problem make antibodies to DNA, or DNA
breakdown products in the embryo or in the pregnancy. These
antibodies form first in the blood as IgM. As the problem gets worse
they appear as IgG and live in the lymphatic system and lymph nodes.
With more losses they form IgA antibodies which have their home and
action in the organs including the uterus. These antibodies can be
against pure double stranded DNA (ds DNA), single stranded DNA (ss
DNA), or smaller molecules called polynucleotides and histones that
make up the single strands (see diagram).
| Autoantibody |
| Double Stranded DNA |
 |
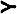 |
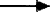 |
Inflammation Around the Placenta |
| Single Stranded DNA |
 |
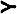 |
| Polynucleotide |
 |
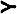 |
| Histone |
 |
 |
Consequences
- Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) positive, speckled pattern.
- Autoantibody to DNA leads to inflammation in the placenta.
- Autoimmune disease screening in the woman is negative (No
evidence of lupus or rheumatoid arthritis).
A blood test determines the presence of antibodies to
polynucleotides, histones and DNA. This process involves running 27
different tests on a sample of blood.
The presence of antibodies is also tested for by doing the ANA
test. This is a less sensitive test but one that many doctors have
already done on their patients before we ever see them.
The test is reported as a titer and a pattern. Any titer above
1:40 is significant. The titers can get into the thousands such as
1:2,500. This simply means that the test is positive when the blood
serum is diluted many times.
The pattern is reported as homogeneous, nucleolar or speckled:
- Homongeneous: the antibody is to the ss DNA or ds DNA.
- Nucleolar: the antibody is directed to the
polynucleotides.
- Speckled: the antibody is directed against the
histones.
Some women demonstrate a mixed pattern of
speckled/homogeneous.
These same antibodies appear positive in women with lupus,
rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease and other autoimmune diseases.
They are usually in high titers. Pregnancy losses, infertility and
IVF failures cause the titers to be much lower and a low positive
titer does not mean that you have or are getting an autoimmune
disease; however, this is ruled out during the testing.
In women with autoimmune diseases these antibodies cause
inflammation in joints and organs. In women with no autoimmune
diseases but a positive antibody, the antibody causes inflammation
around the embryo at the time of implantation or in the placenta
after implantation. This inflammation is exactly the same as occurs
if you get a splinter under your fingernail. The tissue around the
splinter gets hot, red and swollen and it happens quickly.
|