Page 16 - 林口醫研部2021年6月電子報
P. 16
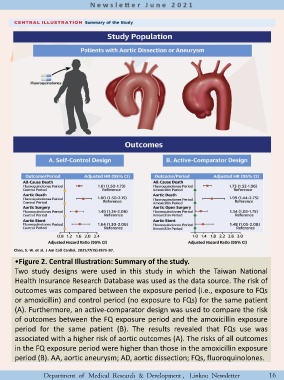
•Figure 2. Central Illustration: Summary of the study.
Two study designs were used in this study in which the Taiwan National
Health Insurance Research Database was used as the data source. The risk of
outcomes was compared between the exposure period (i.e., exposure to FQs
or amoxicillin) and control period (no exposure to FQs) for the same patient
(A). Furthermore, an active-comparator design was used to compare the risk
of outcomes between the FQ exposure period and the amoxicillin exposure
period for the same patient (B). The results revealed that FQs use was
associated with a higher risk of aortic outcomes (A). The risks of all outcomes
in the FQ exposure period were higher than those in the amoxicillin exposure
period (B). AA, aortic aneurysm; AD, aortic dissection; FQs, fluoroquinolones.
Department of Medical Research & Development , Linkou Newsletter 16