Page 20 - 分子轉譯影像中心季刊 IX
P. 20
g’ h’
g” h”
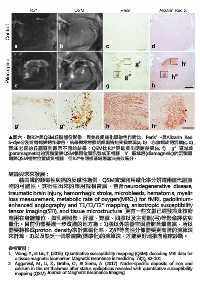
圖六、取R2*與QSM丘腦部份影像,與免疫組織化學染色作對比,Perls’-與Alizarin Red
S-dye分別針對鐵與鈣作染色。結果顯示對照組組織皆無受損表現(a, b),亦無鐵或鈣沉積(c, d);
而SE老鼠的丘腦區則顯示不同的結果:QSM比R2*更能看出明暗差異(e, f),g”區域鐵
(paramagnetic)的沉積量與QSM相同位置訊號成正相關,h’區域鈣(diamagnetic)的沉積量
則與QSM相對位置成負相關,但R2*在同樣區域則無法有效區分。
結論與未來發展:
藉由鐵的順磁性與鈣的反磁性為例,QSM實現利用磁化率分辨這兩種代謝產
物的可能性。其衍生出來的應用就相當廣,包含neurodegenerative disease,
traumatic brain injury, hemorrhagic stroke, microbleeds, hematoma, myelin
loss measurement, metabolic rate of oxygen(MRO ) for fMRI, gadolinium-
2
enhanced angiography and T1/T2/T2* mapping, anisotropic susceptibility
tensor imaging(STI), and tissue microstructure. 更有一些文獻已經發表此技術
應用在身體部位,如乳房照影、肝臟、腎臟、四肢以及主動脈(弓)等影像評估與
量化。目前仍需要進一步改進的地方為:1)腦以外的器官因脂肪含量豐富,所以
需要轉換成proton density來計算磁化率,2)非等向性分佈需要更高階的演算法
來計算,3)以及缺乏一個最適當(標準化)的演算法,才能更好地推向臨床診斷。
參考資料:
1. Wang, Y., & Liu, T. (2015). Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM): decoding MRI data for
a tissue magnetic biomarker. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 73(1), 82-101.
2. Aggarwal, M., Li, X., Gröhn, O., & Sierra, A. (2017). Nuclei‐specific deposits of iron and
calcium in the rat thalamus after status epilepticus revealed with quantitative susceptibility
mapping (QSM). Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging.