Page 61 - 林口長庚醫研部電子報-2018年9月刊
P. 61
NEWSLETTER NEWSLETTER
SEPTEMBER SEPTEMBER
2018 2018
It is noted that warfarin group carried a significantly higher annual risk of Further prospective and randomized controlled validation of our results in
AKI than the dabigatran group for those with high CHA2DS2-VASc score a future study is warranted.
(Figure 2).
We also tried to evaluate the risk of AKI in NVAF Asians taking other
DOACs including apixaban, dabigatran, rivaroxaban as compared with
warfarin. In this nationwide retrospective cohort study, 1,381, 3,863, 6,692
and 5,038 NVAF patients with CKD and 4,146, 18,007, 23,971, and 22,118
NVAF patients without CKD taking apixaban, dabigatran, rivaroxaban,
and warfarin, respectively, from June 1, 2012 to December 31, 2016 were
enrolled from the Taiwan National Health Insurance Program. Propensity-
score weighted method was used to balance covariates across study
groups. Patients were followed until occurrence of AKI or end date of
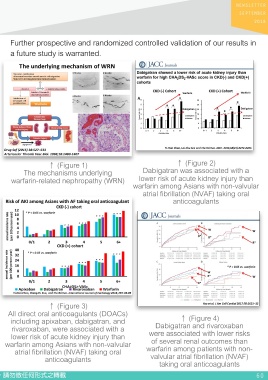
study (December 31, 2016). The results also confirmed that three DOACs ↑ (Figure 1) ↑ (Figure 2)
The mechanisms underlying Dabigatran was associated with a
were all associated with a significantly lower risk of AKI compared with warfarin-related nephropathy (WRN) lower risk of acute kidney injury than
warfarin for both CKD-free (hazard ratio (HR): 0.75, 95%CI: 0.69-0.81 for warfarin among Asians with non-valvular
atrial fibrillation (NVAF) taking oral
apixaban; HR: 0.79, 95%CI: 0.74-0.85 for dabigatran; HR: 0.81, 95% CI: anticoagulants
0.75-0.87 for rivaroxaban) and CKD cohorts (HR: 0.53, 95%CI: 0.45-0.63
for apixaban; HR: 0.63, 95%CI: 0.57-0.69 for dabigatran; HR: 0.63, 95%
CI: 0.58-0.68 for rivaroxaban). No differences in risk of AKI were found
between any two-paired NOACs. The annual incidence of AKI for all
NOACs and warfarin increased gradually as the increment of CHA2DS2-
VASc for both CKD-free and CKD cohorts after propensity score
weighting (Figure 3).
Our results were also supported by other studies showing that dabiagtran
and rivaroxaban were associated with lower risks of several renal
outcomes including more than 30% decline of eGFR, doubling of serum
↑ (Figure 3)
creatinine, and the risk of acute kidney injury (Figure 4). In conclusion, All direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs)
↑ (Figure 4)
use of all DOACs (apixaban, dabigatran, and rivaroxaban), provide for including apixaban, dabigatran, and Dabigatran and rivaroxaban
rivaroxaban, were associated with a
a lower risk of acute kidney injury than warfarin in a large Asian cohort lower risk of acute kidney injury than were associated with lower risks
of several renal outcomes than
patients who did or did not have a history of kidney disease.DOACs may warfarin among Asians with non-valvular warfarin among patients with non-
be a safer alternative to warfarin in Asians with NVAF in terms of the risk atrial fibrillation (NVAF) taking oral valvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF)
anticoagulants
of anticoagulant-related AKI. taking oral anticoagulants
59 非經本刊及作者同意,請勿做任何形式之轉載 60