 |
What is EBP? |
| 1 |
Evidence based
practice (EBP) has many definitions. The most common definition of EBP is
taken from Dr. David Sackett, a pioneer in evidence-based practice.
EBP is "the conscientious, explicit and judicious use of current
best evidence in making decisions about the care of the individual
patient.
(Sacket DL, Rosenberg
WMC, Gray JAM and Richardson WS (1996). Evidence based
medicine: what it is and what it isn't. British Medical
Journal. 312 (13 January 71-72) |
| |

|
It means
integrating individual clinical expertise with the best
available external clinical evidence from systematic
research."
|
|
(http://www.hsl.unc.edu/services/tutorials/ebm/whatis.htm) |
|
2 |
Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
:
Evidence-based practice (EBP) is an interdisciplinary
approach to clinical practice that has been gaining
ground following its formal introduction in 1992. It
started in medicine as
evidence-based medicine
(EBM) and spread to other fields such as
dentistry,
nursing,
psychology,
education, library and
information science and other fields. Its basic
principles are that all practical decisions made should
1) be based on research studies and 2) that these
research studies are selected and interpreted according
to some specific norms characteristic for EBP. Typically
such norms disregard
theoretical studies and
qualitative studies and
consider
quantitative studies
according to a narrow set of criteria of what counts as
evidence. If such a narrow
set of methodological criteria are not applied, it is
better instead just to speak of research based practice.[1]....More
(http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Evidence-based_practice)
(1)Hjrland, Birger (2011).
Evidence based practice: An analysis based on the
philosophy of science. Journal of the American Society
for Information Science and
Technology, 62(7), 1301–1310.
|
| |
|
 |
The goal of EBP
:
*clinical expertise/expert opinion
*external scientific evidence
*client/patient/caregiver
|
 |
| (http://www.asha.org/members/ebp/) |
 |
The
5
Stages of EBP |
|
1 |
ASK-Asking Focused Questions:
translation of uncertainty to an answerable question
→
PICO
(PICO Flowchart)
整理出可以回答的問題
→ 以PICO的方式提出問題
【Patient、Invention、Comparison、Outcome】 (Answering Clinical questions) |
|
2 |
Collect-Finding the Evidence:
systematic retrieval of best
evidence available → 3 steps
找尋最佳證據 →
有3個步驟
*Identify terms to
fit your PICO question
*Look for secondary
sources
【Guidelines、CATs、Evidence-Based Summaries、Structured
Abstracts、Systematic Reviews】
*Search for Primary
Sources〔PubMED〕 |
|
3 |
Appraise-Critical Appraisal:
testing evidence for
validity, clinical relevance, and applicability
嚴格評讀證據 → 證據等級【Levels of EBM】(www.cebm.net) |
|
4 |
Integrate-Making a Decision:
application of results in
practice
整合文獻證據,應用於病人身上
*Define the
population and intervention
*Search for and
understand the biases
*Interpret the
findings and apply them to your patient |
|
5 |
Evaluate-Evaluating Performance:auditing evidence-based decisions
針對上述四點進行評估 |

|
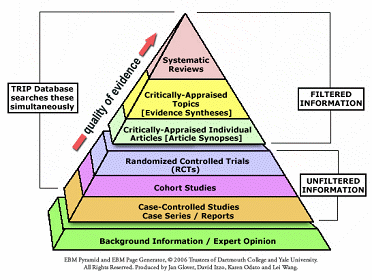
Hierarchy of Evidence-Based Medicine (EBM) Resources
Evidence-Based Medicine is the integration of best
research evidence with clinical expertise and patient
values. (Sackett
DL, Straus SE, Richardson WS, et al. Evidence-based
medicine: how to practice and teach EBM. 2nd ed.
Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 2000.)
*Systematic reviews (including meta analysis)
*Randomised
controlled trials (RCTs & other experimental
research)
n
n*Non-randomised
controlled trials
n*Case
controlled trials
n*Cohort
studies
n*Descriptive
studies
n*Qualitative
studies
n*Expert
opinion
|
The
Evidence Pyramid
 |
| |
|
|
| |
(http://www.mclibrary.duke.edu/subject/ebm/ebmpyramid.html)
|
.gif)
.gif)