|
 |
What is EBN? |
|
|
1 |
Evidence based nursing, or EBN, is a
form of clinical practice that relies on research findings to manage
the health problems of a patient. It involves several processes that
can contribute to a better understanding of a patient’s condition as
well as the effectiveness of a certain treatment method. Evidence
based nursing usually begins with the formulation of a question
concerning a patient’s medical condition, and then, research is
performed to find answers to the question. The relevancy of the
research has to be proven and alternative forms of medical care have
to be considered before evidence based practice is implemented.
(http://www.nursegroups.com )
國際護理榮譽學會(Sigma Theta Tau International,
2004)的定義:
實證護理為涵蓋現有之最佳證據及護理實務經驗,並重視個人及所屬家庭及社區之價值及偏好的護理照護。
|
|
|
2 |
Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
:
Evidence-Based Nursing or EBN is a type of
evidence-based healthcare, drawing on some of the traditions of
evidence-based medicine. It involves identifying solid research
findings and implementing them in
nursing practices, in order to increase the quality of patient
care. The goal of EBN is to provide the highest quality and most
cost-efficient nursing care possible. EBN is a process founded on
the collection, interpretation, and integration of valid, important,
and applicable research. Some define EBN tightly, considering only
the application of the findings of
randomized clinical trials, while others also include the use of
case reports and expert opinions.[1]
In order to practice evidence based nursing, practitioners must
understand the concept of research and know how to accurately
evaluate this research. These skills are taught in modern nursing
education and also as part of professional training....More
(http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Evidence-based_nursing)
(1)LoBiondo-Wood,
G., & Haber, J. (2006). Nursing Research: Methods and Critical
Appraisal for Evidence-Based Practice. St. Louis, Missouri:
Mosby Elsevier.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
實證護理的目的(Closs & Cheater, 1999 ; Rycroft-Malone,
Bucknall & Melnyk, 2004):
1
提供最佳的照顧方式
2
維護病人的安全及最大利益
3
降低成本
|
|
|
|
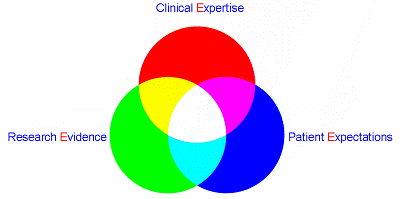
三個〔E〕的整合,以提供病人最安全及能符合期望的一種臨床工作方式及態度。
*最佳文獻證據(Evidence)
•*醫護人員的經驗(Experience)
*病人的期望(Expectations)
|
 |
|
|
 |
The Steps in the EBN Process |
|
|
|
|
1 |
Formulating a searchable question→
PICO
|
(領導護理 2005;6(1):p.8-15) |
| |
整理出一個可以回答的問題
|
|
2 |
Searching the literature
efficiently |
|
|
找出最佳文獻證據
|
|
3 |
Appraising the literature critically |
|
|
嚴格判讀文獻→信效度、可推廣性
|
|
4 |
Applying the result to clinical practice or patient |
|
|
整理文獻證據,應用於病人身上
(臨床實務)
|
|
5 |
Evaluating the outcomes of the applied evidence in your
practice or patient |
|
|
針對以上步驟,進行臨床稽核(評估效果)
|
|
|
 |
證據分級系統: |
|
|
|
一般常用的證據分類系統如下:
Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network
American College of Chest Physicians
Oxford Centre for Evidence-based Medicine
Australian National Health and Medical Research Council
US Task Force on Community Preventive Services
(如何撰寫臨床指引/林菁華,蔡伶觀, p.61-63) |
|
| |
* Oxford Classification (Center for
Evidence-Based Medicine, 2001)(www.cebm.net)
以臨床問題類型為主的證據等級
|
Grade
of Recommendation
建議分級 |
Level
of Evidence
證據等級 |
Therapy/Prevention
治療或措施 |
|
〔A〕 |
1a |
Systemic
review of RCTs
隨機控制試驗的系統性文獻回顧 |
|
|
1b |
Single
RCT
單一隨機控制試驗 |
|
|
1c |
All-or-none
有一致性結果的個案報告 |
|
〔B〕 |
2a |
Systemic
review of cohort studies
世代性研究的系統性文獻回顧 |
|
|
2b |
Cohort
study or poor RCT
世代性研究或較不嚴謹的隨機控制試驗 |
|
|
2c |
Outcomes
research
成效研究 |
|
|
3a |
Systemic
review of case-control studies
病歷對照研究系統性文獻回顧 |
|
|
3b |
Case-control study
病歷對照研究 |
|
〔C〕 |
4 |
Case
series
個案報告 |
|
〔D〕 |
5 |
Expert
opinion, physiology, bench research
綜論 |
|
|
| |
*
Melnyk和Fineout-Overholt (2005)
|
|
|
|
|
隨機控制試驗的系統性文獻回顧、統合分析或以隨機控制試驗的系統性文獻回顧為基礎發展的實證臨床照護指引
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
* 中央健康保險局 (2004)
SIGN和NICE4所採用以研究設計類型為主的證據等級,證據等級的分類如下:
|
等級 |
實證類別 |
|
1++ |
高品質之整合分析(meta
analysis),系統性文獻回顧(systematic reviews)之隨機控制試驗(RCTs),或該隨機控制試驗之設計誤差(bias)極低. |
|
1+ |
執行良好之整合分析(meta
analysis),系統性文獻回顧(systematic reviews)之隨機對照試驗(RCTs),或該隨機控制試驗之設計誤差(bias)極低. |
|
1- |
整合分析(meta
analysis)系統性文獻回顧(systematic reviews)之隨機對照試驗(RCTs),或該隨機控制試驗之設計誤差(bias)偏高. |
|
2++ |
1. 經過病例對照研究(case-control
study)或世代研究(cohort study)之高品質系統性文獻回顧.
2. 高品質的病例對照研究法及世代研究法可降低干擾、誤差及機率,並且具有高度的因果相關. |
|
2+ |
經過病例對照研究(case-control
study)或世代研究(cohort study)之設計良好的系統性文獻回顧. |
|
2- |
研究誤差(bias)較高之病例對照研究或世代研究. |
|
3 |
非分析性之研究,例如:個案報告. |
|
4 |
專家意見 |
|
|
SIGN:Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network
NICE:National Institute for Health and Clinical
Excellence |
|
|
|
.gif)
.gif)
