 |
What is EBM?
|
| |
1 |
Sackett, et al. :
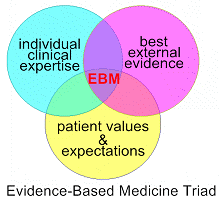
Evidence-Based Medicine (EBM) is “the integration of best research evidence with
clinical expertise and patient values.” (Sackett D et al. Evidence-Based Medicine:
How to Practice and Teach EBM, 2nd edition. Churchill
Livingstone, Edinburgh, 2000, p.1) |
| |
|
*by best evidence
*by clinical expertise
*by clinical expectation
(http://ktclearinghouse.ca/cebm/intro/whatisebm) |
 |
|
| |
| |
2 |
The EBM Working Group
:
EBM is nothing more than
a process of life-long, self-directed learning in which
caring for patients creates the need for clinically
important information about diagnosis, prognosis,
therapy, and other clinical and health care issues
( http://researchguides.uic.edu/ebm) |
|
| |
3 |
Doherty, Steve. "Evidence-based medicine: Arguments for
and Against." Emergency Medicine Australasia 2005; 17:
307-13.
EBM is…
“an
evolutionary progression of knowledge based on the basic
and clinical sciences and facilitated by the age of
information technology.”
(http://researchguides.uic.edu/ebm) |
| |
4 |
Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
:
Evidence-based medicine (EBM) (sometimes
called evidence-based health care or EBHC
to broaden its application to allied health care
professionals) has been defined as "the conscientious,
explicit an judicious use of current best evidence in
making decisions about the care of individual patients."[1][2]
Trisha Greenhalgh and
Anna Donald define it
more specifically as "the use of mathematical estimates
of the risk of benefit and harm, derived
from high-quality research on population samples, to
inform clinical decision-making in the diagnosis,
investigation or management of individual patients."[3]
...More
(http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Evidence-based_medicine)
(1)Sackett
DL, Rosenberg WM, Gray JA, Haynes RB, Richardson WS
(January 1996).
"Evidence based medicine: what it is and what it
isn't"BMJ
312
(7023): 71–2.
(2)Timmermans
S, Mauck A (2005).
"The promises and pitfalls of
evidence-based medicine".
Health Aff (Millwood)
24
(1): 18–28.
(3)Greenhalgh,
Trisha. How To Read a Paper: The Basics of
Evidence-Based Medicine. Wiley-Blackwell, fourth
edition, 2010, p. 1.
|
| |
|
 |
The
Five Steps of EBM
(www.cebm.net)
實證醫學的5步驟 (Sackett, 2000) |
| |
1 |
Asking Focused Questions:
translation of uncertainty to an answerable question
→
PICO
(PICO Flowchart)
整理出可以回答的問題
→ 以PICO的方式提出問題
【Patient、Invention、Comparison、Outcome】 (Answering Clinical questions)
(Sackett
DL, Richardson WS, Rosenberg W, Haynes RB (1997).
Evidence-based medicine: How to practice and teach EBM.
New York: Churchill Livingston) |
| |
|
|
Defining a clinical question in terms of the
specific patient problem aids the searcher
in finding clinically relevant evidence in
the literature.
( http://researchguides.uic.edu/ebm
) |
|
PICO. Model
|
|
P |
I |
C |
O |
|
Population/patient |
Intervention/indicator |
Comparator/control |
Outcome |
The population or problem you are interested in (client group,
problem)
|
The intervention that you are interested in
|
The comparison or alternative
intervention (if relevant)
|
The outcome
or reason for using the intervention
|
|
(Amy Baker
& Melissa Edwards, University of South
Australia) |
|
| |
2 |
Finding the Evidence:
systematic retrieval of best
evidence available → 3 steps
找尋最佳證據 →
有3個步驟
*Identify terms to
fit your PICO question
*Look for secondary
sources
【Guidelines、CATs、Evidence-Based Summaries、Structured
Abstracts、Systematic Reviews】
*Search for Primary
Sources〔PubMED〕 |
| |
3 |
Critical Appraisal:
testing evidence for
validity, clinical relevance, and applicability
嚴格評讀證據 → 證據等級【Levels of EBM
2011 、2009】(www.cebm.net) |
|
| |
4 |
Making a Decision:
application of results in
practice
整合文獻證據,應用於病人身上
*Define the
population and intervention
*Search for and
understand the biases
*Interpret the
findings and apply them to your patient |
|
| |
5 |
Evaluating Performance:auditing evidence-based decisions
針對上述四點進行評估 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
.gif)
.gif)