Loss of the Mucous Plug, Bloody Show

During pregnancy, thick mucous fills the opening of the cervix. As the cervix chagnes shape in preparation for labor, this mucous is released. It may appear tinged with blood. This can happen moments, days or weeks before labor begins.
During labor, many women experience Bloody Show. As the cervix expands and dilates, small capillaries are broken and produces bloodyshow.
Effacement and Dilation
First, prostaglandins and other hormones soften the cervix, preparing it for labor. During the first stage of labor, contraction efface (thin out) and dilate (open) the cervix.
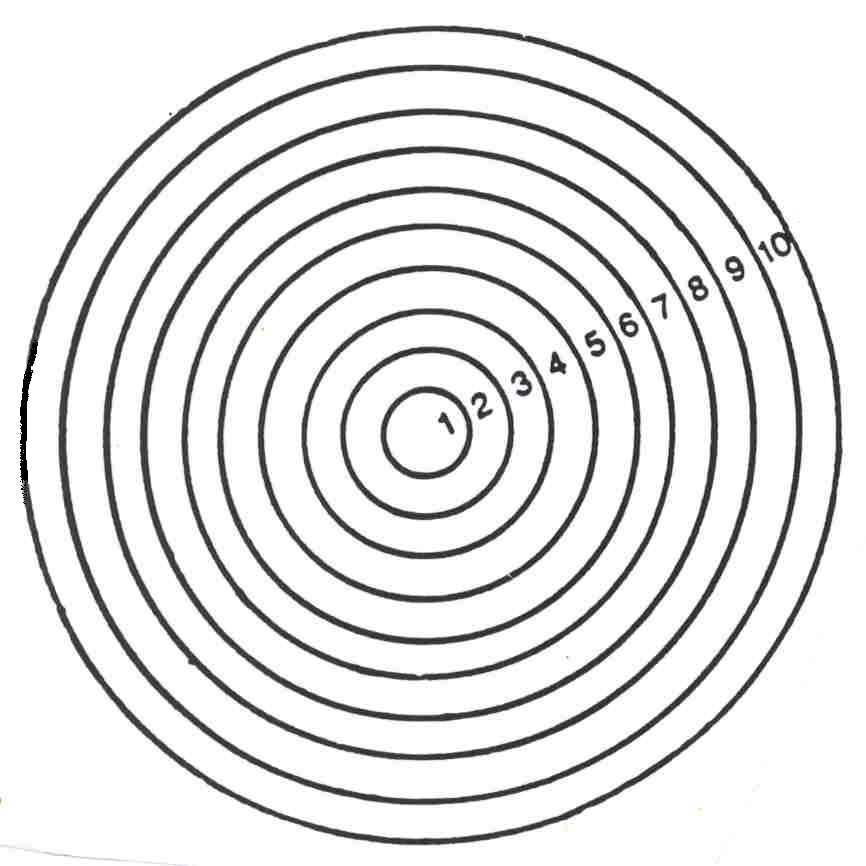
During a pelvic exam your health care provider can tell you the status of your cervix.
Dilation is measured in centimeters from 0-10. When your cervix is fully dilated (10 cm), the second stage of labor begins.
The image to the right demonstrates in actual diameter in centimeters.
|
No changes to cervix |
0% effaced |
|
Cervix is half its normal length |
50% effaced |
|
Cervix is completely thinned out. |
100% effaced |
¡@
Rupture of the Membranes, "Water Breaking"


The sac that the baby has been growing in is filled with amniotic fluid. This fluid acts as a protective shock absorber and maintains a constant temperature and environment for the baby. The sac can rupture at the onset of labor, or at any time during labor. Sometimes, the membrane will be ruptured by the health care provider during labor or birth. If your sac breaks or starts leaking before you arrive at the hospital, call your health care provider.
Many women are unsure if their membranes have ruptured or if they inadvertently urinated. Use this little graph as an aid.
|
Fluid Type |
Color |
Odor |
|
|
Amniotic Fluid |
clear |
none |
will not stop flow |
|
Urine |
yellow |
yes |
will stop fluid |
Contractions, False Labor
The muscle fibers of the uterus can contract or shorten, making the uterus feel hard. The uterus uses contractions to do the work of labor. Braxton-Hicks contractions are the tightening of the uterine muscles that occurs througout pregnancy. In late pregnancy Braxton-Hicks contractions can feel so intense they can be mistaken fro labor contractions. This called "false labor". These contractions are usually irregular, have no predictable pattern and go away if activity is changed. Before 37 weeks of pregnancy, notify your health care provider if you feel five or more contractions in an hour.
How to distinguish true labor from false labor
|
True Labor |
False Labor |
|
|
Contractions |
get closer together, at regular intervals, intensity progresses |
unpredicatable, vary in intensity and frequency |
|
Activity |
Contractions continue or become more intense with change in activity |
Go away with activity or change in position |
|
Cervical Changes |
cervix dilates and effaces; bloody show |
No change in cervical status |
