巴拉刈中毒(paraquat intoxication)
巴拉刈農藥是劇毒,濃度20%的巴拉刈只要15 mL就足以造成死亡,中毒病人會口腔潰爛、多重器官衰竭、肺部纖維化、並在二至三週時因缺氧而死亡。林杰樑教授率先提出了巴拉刈中毒的有效治療方法,他採用重覆類固醇及免疫抑制劑脈衝療法,再加上即時的活性碳血液灌流除汙,大幅度降低了病人的死亡率,存活率更高達50~60%。這種方法已為許多國家採用,也被列為巴拉刈中毒的標準治療方法,有多家權威實證醫學機構,認為這是目前為止唯一對巴拉刈中毒有效的療法。相關研究除撰寫過教科書外,亦發表了一系列論文於許多國際期刊如美國呼吸及重症照護、重症醫學、胸腔醫學等等。
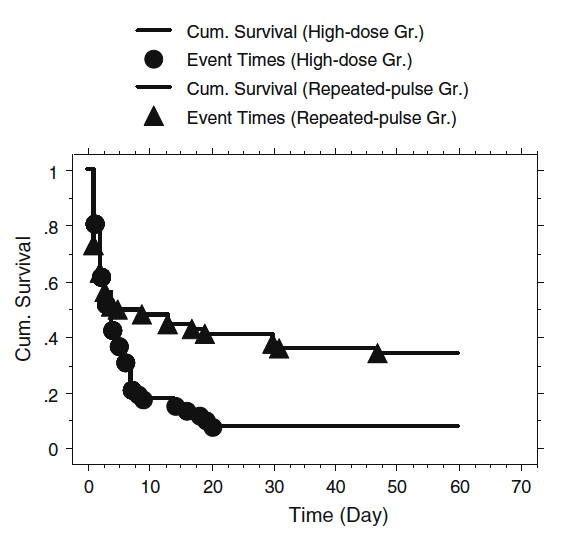
圖二、接受重覆類固醇及免疫抑制劑脈衝療法的巴拉刈中毒病人,存活率會較沒有接受螯合劑治療的高。(Intensive Care Med. 2011 Jun;37(6):1006-13)
團隊發表之相關國際期刊論文:
1.Weng CH, Chen HH, Hu CC, Huang WH, Hsu CW, Fu JF, Lin WR, Wang IK, Yen TH. Predictors of acute kidney injury after paraquat intoxication. Oncotarget (Epub ahead of print)
2.Wu MY, Hsu MY, Chen SJ, Hwang DK, Yen TH, Cheng CM. Point-of-Care Detection Devices for Food Safety Monitoring - Proactive Disease Prevention. Trends Biotechnol. 2017;35:288-300
3.Kuan CM, Lin ST, Yen TH, Wang YL, and Cheng CM. Paper-based diagnostic devices for clinical paraquat poisoning diagnosis. Biomicrofluidics 2016;10:034118
4.Lin C, Yen TH, Juang YY, Lin JL, Lee SH. Psychiatric comorbidity and its impact on mortality in patients who attempted suicide by paraquat poisoning during 2000-2010. PLoS One. 2014;9:e112160.
5.Weng CH, Hu CC, Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Hsu CW, Yen TH. Predictors of acute respiratory distress syndrome in patients with paraquat intoxication. PLoS One. 2013;8:e82695.
6.Chen HH, Lin JL, Huang WH, Weng CH, Lee SY, Hsu CW, Chen KH, Wang IK, Liang CC, Chang CT, Yen TH. Spectrum of corrosive esophageal injury after intentional paraquat or glyphosate-surfactant herbicide ingestion. Int J Gen Med. 2013;6:677-83.
7.Hsieh YW, Lin JL, Lee SY, Weng CH, Yang HY, Liu SH, Wang IK, Liang CC, Chang CT, Yen TH. Paraquat poisoning in pediatric patients. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2013;29:487-91.
8.Weng CH, Hu CC, Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Huang WH, Hsu CW, Yen TH. Sequential organ failure assessment score can predict mortality in patients with paraquat intoxication. PLoS One. 2012;7:e51743.
9.Hsu CW, Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Chen KH, Yen TH, Wu MS, Lin SC. Early hemoperfusion may improve survival of severely paraquat-poisoned patients. PLoS One. 2012;7:e48397.
10.Yang CJ, Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Weng CH, Hsu CW, Lee SY, Lee SH, Chang CM, Lin WR, Yen TH. Spectrum of toxic hepatitis following intentional paraquat ingestion: analysis of 187 cases. Liver Int. 2012;32:1400-6.
11.Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Chen KH, Huang WH, Hsu CW, Hsu HH, Yen TH. Improved survival in severe paraquat poisoning with repeated pulse therapy of cyclophosphamide and steroids. Intensive Care Med. 2011; 37:1006-13.
12.Yen TH, Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Hsu CW, Weng CH, Chen YH. Spectrum of corrosive esophageal injury after intentional paraquat ingestion. Am J Emerg Med. 2010;28:728-33.
13.Tsai TY, Weng CH, Lin JL, Yen TH. Suicide victim of paraquat poisoning make suitable corneal donor. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2011;30:71-3.
14.Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Chen KH, Huang WH. Repeated pulse of methylprednisolone and cyclophosphamide with continuous dexamethasone therapy for patients with severe paraquat poisoning. Crit Care Med. 2006;34:368-73.
15.Jenq CC, Wu CD, Lin JL. Mother and fetus both survive from severe paraquat intoxication. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2005;43:291-5.
16.Lin NC, Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Yu CC. Combined initial cyclophosphamide with repeated methylprednisolone pulse therapy for severe paraquat poisoning from dermal exposure. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 2003;41:877-81.
17.Hsu HH, Chang CT, Lin JL. Intravenous paraquat poisoning-induced multiple organ failure and fatality--a report of two cases. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 2003;41:87-90.
18.Chen GH, Lin JL, Huang YK. Combined methylprednisolone and dexamethasone therapy for paraquat poisoning. Crit Care Med. 2002;30:2584-7.
19.Lin JL, Leu ML, Liu YC, Chen GH. A prospective clinical trial of pulse therapy with glucocorticoid and cyclophosphamide in moderate to severe paraquat-poisoned patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;159:357-60.
20.Lin JL, Wei MC, Liu YC. Pulse therapy with cyclophosphamide and methylprednisolone in patients with moderate to severe paraquat poisoning: a preliminary report. Thorax. 1996;51:661-3.
21.Lin JL, Liu L, Leu ML. Recovery of respiratory function in survivors with paraquat intoxication. Arch Environ Health. 1995;50:432-9.
