低劑量鉛暴露引起之慢性腎臟疾病(low dose lead exposure related chronic kidney disease)
當病人的腎功能惡化是鉛污染造成時,適時給予螯合劑治療,可以降低血液中鉛濃度,也能有效減緩腎功能惡化。過去20多年來,團隊在林杰樑教授的帶領下,已陸續發表了一系列關於長期暴露於低劑量鉛對慢性腎病惡化的論文於國際期刊,包括新英格蘭醫學雜誌、內科醫學年鑑、美國腎臟病學會雜誌等等。
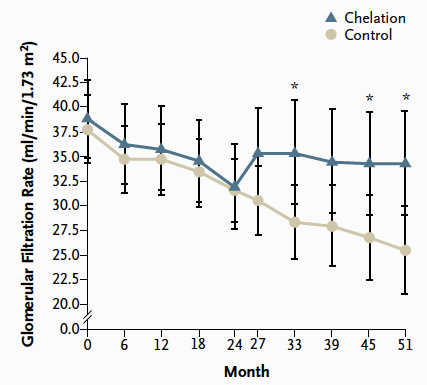
圖一、接受螯合劑治療的鉛中毒病人,腎絲球過濾率會較沒有接受螯合劑治療有改善。(N Engl J Med. 2003 Jan 23;348(4):277-86)
團隊發表之相關國際期刊論文:
1.Weng CH, Hsu CW, Hu CC, Yen TH, Chan MJ, Huang WH. Blood lead level is a positive predictor of uremic pruritus in patients undergoing hemodialysis. Ther Clin Risk Manag 2017:13;717-23
2.Chen CY, Liu MH, Hsu CW, Weng CH, Yen TH, Huang WH. Positive correlation between environmental PM2.5 and blood lead levels in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis. Ther Clin Risk Manag 2017;13:555-64
3.Huang WH, Hsu CW, Weng CH, Lin-Tan DT, Yen TH. Negative Relationship between Erythropoietin Dose and Blood Lead Level in Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis. Sci Rep 2016;6:34313
4.Huang WH, Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Hsu CW, Chen KH, Yen TH. Environmental lead exposure accelerates progressive diabetic nephropathy in type II diabetic patients. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:742545.
5.Wu HM, Lin-Tan DT, Wang ML, Huang HY, Lee CL, Wang HS, Soong YK, Lin JL. Lead level in seminal plasma may affect semen quality for men without occupational exposure to lead. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2012;10:91.
6.Chen KH, Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Hsu HH, Hsu CW, Hsu KH, Yen TH. Effect of chelation therapy on progressive diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes and high-normal body lead burdens. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012;60:530-8.
7.Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Hsu CW, Yen TH, Chen KH, Hsu HH, Ho TC, Hsu KH. Association of blood lead levels with mortality in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Am J Med. 2011;124:350-8.
8.Yen TH, Lin-Tan DT, Lin JL. Chronic renal failure induced by lead. Kidney Int. 2011;79:688.
9.Yen TH, Lin JL, Weng CH, Tang CC. Colic induced by lead. CMAJ. 2010;182:E381.
10.Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Chen KH, Hsu CW, Yen TH, Huang WH, Huang YL. Blood lead levels association with 18-month all-cause mortality in patients with chronic peritoneal dialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25:1627-33.
11.Lee TH, Tseng MC, Chen CJ, Lin JL. Association of high body lead store with severe intracranial carotid atherosclerosis. Neurotoxicology. 2009;30):876-80.
12.Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Yen TH, Hsu CW, Jenq CC, Chen KH, Hsu KH, Huang YL. Blood lead levels, malnutrition, inflammation, and mortality in patients with diabetes treated by long-term hemodialysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008;51:107-15.
13.Lin-Tan DT, Lin JL, Yen TH, Chen KH, Huang YL. Long-term outcome of repeated lead chelation therapy in progressive non-diabetic chronic kidney diseases. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007;22:2924-31.
14.Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Li YJ, Chen KH, Huang YL. Low-level environmental exposure to lead and progressive chronic kidney diseases. Am J Med. 2006;119:707.e1-9.
15.Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Yu CC, Li YJ, Huang YY, Li KL. Environmental exposure to lead and progressive diabetic nephropathy in patients with type II diabetes. Kidney Int. 2006;69:2049-56.
16.Yu CC, Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT. Environmental exposure to lead and progression of chronic renal diseases: a four-year prospective longitudinal study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15:1016-22.
17.Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Hsu KH, Yu CC. Environmental lead exposure and progression of chronic renal diseases in patients without diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:277-86.
18.Lin JL, Tan DT, Ho HH, Yu CC. Environmental lead exposure and urate excretion in the general population. Am J Med. 2002;113:563-8.
19.Lin JL, Yu CC, Lin-Tan DT, Ho HH. Lead chelation therapy and urate excretion in patients with chronic renal diseases and gout. Kidney Int. 2001;60:266-71.
20.Lin JL, Tan DT, Hsu KH, Yu CC. Environmental lead exposure and progressive renal insufficiency. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161:264-71.
21.Lin JL, Ho HH, Yu CC. Chelation therapy for patients with elevated body lead burden and progressive renal insufficiency. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1999;130:7-13.
22.Lin JL, Shih FC. Reversible hypothyroidism with EDTA chelation therapy in a patient with elevated lead burden and chronic renal insufficiency. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1997;12:364-5.
23.Lin JL, Lim PS. Does lead play a role in the development of renal insufficiency in some patients with essential hypertension? J Hum Hypertens. 1994;8:495-500.
24.Lin JL, Huang PT. Body lead stores and urate excretion in men with chronic renal disease. J Rheumatol. 1994;21:705-9.
25.Lin JL, Yeh KH, Tseng HC, Chen WY, Lai HH, Lin YC. Urinary N-acetyl-glucosaminidase excretion and environmental lead exposure. Green Cross Health Service Association Study Group. Am J Nephrol. 1993;13:442-7.
26.Lin JL, Lim PS. Elevated lead burden in Chinese patients without occupational lead exposure. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1992;18:1-5.
